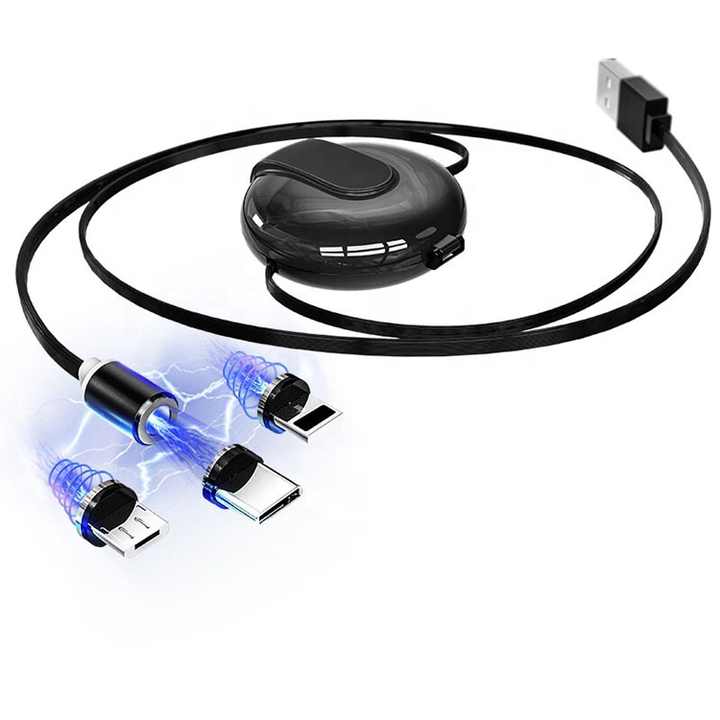
Los cables USB retráctiles combinan la comodidad de un almacenamiento compacto con una transferencia fiable de datos y energía. Para entender cómo funcionan estos cables, es esencial explorar su diseño mecánico, arquitectura eléctrica y cumplimiento de los protocolos de comunicación USB.
1. Componentes principales y diseño mecánico
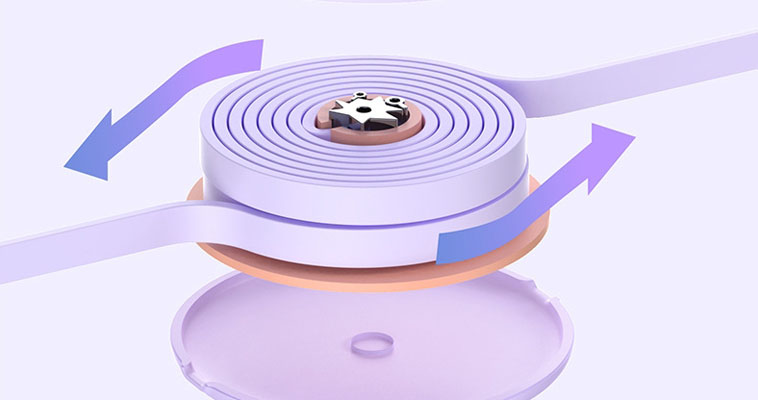
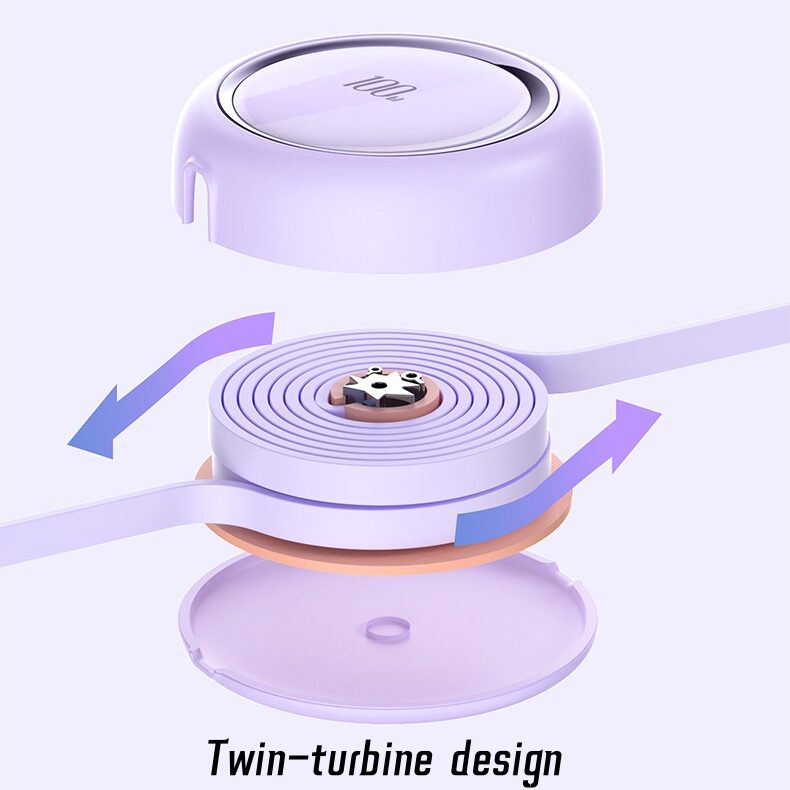
Los cables USB retráctiles integran un mecanismo de bobina con resorte alojado en una carcasa compacta. Este mecanismo permite que el cable se extienda hasta una longitud fija (normalmente 0,5-1 metros) y se retraiga suavemente cuando no se utiliza. Los componentes clave son:
- Carrete de resorte: Un muelle de torsión controla la retracción, garantizando el equilibrio de la tensión durante la extensión y el retroceso.
- Alambres de cinta conductores: A diferencia de los alambres redondos estándar, los conductores planos tipo cinta se utilizan a menudo para reducir la fricción y el desgaste durante el bobinado repetido.
- Capas de durabilidad: Los cables internos están blindados con un aislamiento flexible (por ejemplo, elastómeros termoplásticos) para soportar los esfuerzos de flexión.
2. Funcionalidad eléctrica y comunicación USB
Los cables retráctiles cumplen las normas USB, lo que garantiza la compatibilidad con los dispositivos. Así es como mantienen la integridad de la señal:
- Señalización diferencial: La comunicación USB se basa en dos líneas de datos (D+ y D-) que transmiten señales complementarias para minimizar las interferencias electromagnéticas (EMI). Esto es fundamental en diseños retráctiles, donde el enrollamiento de los cables podría amplificar el ruido.
- Suministro de energía: Las líneas VCC y GND de 5 V proporcionan alimentación, con cables retráctiles que admiten velocidades USB 2.0 (480 Mbps) o USB 3.0 (5 Gbps) en función de la calidad del blindaje.
- Sincronización: Los cables USB 3.0+ pueden incluir pares trenzados adicionales para una comunicación full-duplex, aunque los diseños retráctiles priorizan la flexibilidad y suelen limitarse a las especificaciones USB 2.0.
| Característica | USB 2.0 retráctil | USB 3.0 retráctil |
|---|---|---|
| Velocidad máxima de datos | 480 Mbps | 5 Gbps |
| Potencia de salida | 500 mA | 900 mA |
| Caso típico | Carga, periféricos | Almacenamiento externo, vídeo HD |
3. Retos y compensaciones
Aunque los cables retráctiles destacan por su portabilidad, se enfrentan a limitaciones técnicas:
- Degradación de la señal: El bobinado repetido puede estresar los conductores, aumentando la resistencia y reduciendo la velocidad de transmisión de datos con el tiempo.
- Límites de durabilidad: Los componentes mecánicos (por ejemplo, los muelles) pueden desgastarse tras miles de ciclos.
- Restricciones de longitud: Los cables retráctiles más largos corren el riesgo de enredarse y reducir la eficacia del retroceso.
4. Buenas prácticas para los usuarios
- Evitar la sobreextensión: Exceder la longitud del cable puede dañar los hilos internos.
- Inspección periódica: Compruebe si hay deshilachado o rigidez cerca de la bobina, lo que indica desgaste.
- Uso para tareas ligeras: Ideal para dispositivos de carga o de bajo ancho de banda; evita las transferencias de datos a alta velocidad que requieren estabilidad USB 3.0+.
Conclusión
Los cables USB retráctiles aprovechan la ingeniería de precisión para equilibrar portabilidad y funcionalidad. Al comprender su diseño mecánico y eléctrico, los usuarios pueden optimizar el rendimiento y mitigar los problemas relacionados con el desgaste. A medida que evolucionan los estándares USB-C y otros más rápidos, los futuros diseños retráctiles pueden incorporar materiales avanzados como el aislamiento de polímero de cristal líquido (LCP) para mejorar la durabilidad y la velocidad.