Introducción
Cables USB son una parte esencial de la tecnología moderna, ya que permiten la transferencia de datos, la carga de dispositivos y la conexión de periféricos. Sin embargo, con tantos tipos de cables USB disponibles, puede resultar confuso saber cuál es el más adecuado para sus necesidades. En esta entrada del blog, exploraremos los diferentes tipos de cables USB, incluyendo Micro USB, USB-A, USB-B, USB-Cy el último USB4 estándar. Para que sea más fácil de entender, también incluiremos una tabla comparativa para destacar sus principales diferencias. Al final, sabrá qué cable elegir en función de los requisitos de su dispositivo.
1. ¿Qué es un cable USB?
Cables USB (Universal Serial Bus) es un cable estándar utilizado para transferir datos entre dispositivos, cargar aparatos y conectar periféricos. Los distintos tipos de cables USB se definen por sus conectores y las capacidades de transferencia de datos y alimentación que admiten. A lo largo de los años, los cables USB han evolucionado desde los conectores básicos hasta versiones más avanzadas que ofrecen velocidades más rápidas y mayor suministro de energía.
2. Los principales tipos de cables USB
Veamos los distintos cables USB con los que es más probable que te encuentres:
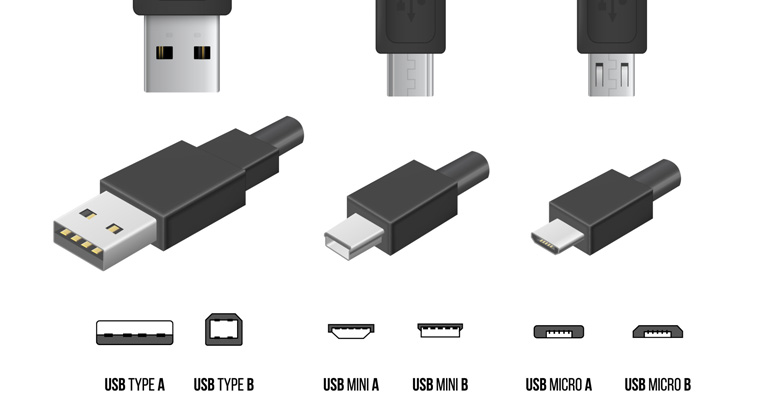
USB-A: el conector tradicional
- Descripción: USB-A es el clásico conector USB rectangular que se ha utilizado ampliamente durante años. A menudo encontrarás puertos USB-A en ordenadores antiguos, portátiles y diversos periféricos USB.
- Velocidad: USB 2.0 (480 Mbps), USB 3.0/3.1 (5-10 Gbps).
- Úsalo: Se utiliza principalmente para conectar teclados, ratones, impresoras y otros accesorios a un ordenador.
- Limitaciones: No es reversible; sólo admite una entrega de potencia inferior en comparación con las normas más recientes.
Micro USB: Conector pequeño para dispositivos antiguos
- Descripción: Los conectores micro USB son más pequeños que los USB-A y se utilizan ampliamente en teléfonos inteligentes, tabletas y diversos gadgets.
- Velocidad: USB 2.0 (480 Mbps), con algunas versiones compatibles con velocidades USB 3.0 (hasta 5 Gbps).
- Úsalo: Se utiliza habitualmente para cargar y transferir datos en smartphones antiguos, dispositivos portátiles y periféricos como mandos de juegos.
- Limitaciones: Carga y transferencia de datos más lentas en comparación con los estándares más recientes; cada vez más eliminado en favor de USB-C.
USB-B: Conector para impresoras y dispositivos grandes
- Descripción: USB-B es un conector de forma cuadrada que suele utilizarse para dispositivos de mayor tamaño, como impresoras y discos duros externos.
- Velocidad: USB 2.0 (480 Mbps) y USB 3.0 (hasta 5 Gbps).
- Úsalo: Suele encontrarse en aparatos de oficina o industriales.
- Limitaciones: Uso limitado en electrónica de consumo; voluminoso para dispositivos portátiles.
USB-C: El conector moderno y versátil
- Descripción: USB-C es el último estándar USB, conocido por su diseño pequeño y reversible que funciona tanto con alimentación como con datos.
- Velocidad: USB 3.1 (10 Gbps) y USB4 (hasta 40 Gbps).
- Úsalo: Carga rápida, transferencia de datos a alta velocidad y salida de vídeo. USB-C es ahora el estándar para la mayoría de dispositivos modernos, incluidos smartphones, portátiles y tabletas.
- Ventajas:
- Reversible, para que sea más fácil enchufarlo.
- Admite mayores velocidades de transferencia de datos y más potencia (hasta 100 W).
- Puede transportar señales de vídeo (DisplayPort, HDMI) junto con datos y alimentación.
- Limitaciones: Aunque la mayoría de los dispositivos nuevos utilizan USB-C, es posible que los más antiguos sigan necesitando adaptadores.
USB4: el futuro de la conectividad USB
- Descripción: USB4 es el último y más rápido estándar USB. Ofrece velocidades de transferencia de datos aún mayores, mayor suministro de energía y compatibilidad mejorada.
- Velocidad: Hasta 40 Gbps.
- Úsalo: Ideal para dispositivos de gama alta que requieren una transferencia de datos extremadamente rápida, como PC para juegos, salida de vídeo 4K/8K y almacenamiento ultrarrápido.
- Ventajas: Conectividad preparada para el futuro con compatibilidad Thunderbolt, transferencia de datos a muy alta velocidad y suministro de energía versátil.
- Limitaciones: Todavía en fase de adopción temprana para muchos dispositivos.
3. Tabla comparativa de cables USB
Para facilitar la comprensión de las diferencias, he aquí una tabla que resume las principales características de cada tipo de cable USB:
| Tipo USB | Forma del conector | Velocidad | Potencia máxima | Caso práctico | ¿Reversible? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB-A | Rectangular | USB 2.0 (480 Mbps), USB 3.0/3.1 (5-10 Gbps) | Hasta 2,5 W | Conexión de periféricos (teclados, ratones, impresoras) | No |
| Micro USB | Pequeño, cónico | USB 2.0 (480 Mbps), USB 3.0 (5 Gbps) | Hasta 2,5 W | Carga y transferencia de datos (smartphones, tabletas) | No |
| USB-B | Cuadrado | USB 2.0 (480 Mbps), USB 3.0 (5 Gbps) | Hasta 2,5 W | Impresoras, escáneres, discos duros externos | No |
| USB-C | Oval, reversible | USB 3.1 (10 Gbps), USB4 (40 Gbps) | Hasta 100 W | Dispositivos modernos (teléfonos inteligentes, ordenadores portátiles, tabletas) | Sí |
| USB4 | Oval, reversible | Hasta 40 Gbps | Hasta 100 W | Dispositivos de alto rendimiento, vídeo 4K/8K | Sí |
4. ¿Qué cable USB elegir?
A la hora de decidir qué cable USB le conviene, tenga en cuenta lo siguiente:
- Compatibilidad de dispositivos: Asegúrate de que el cable se adapta tanto a tu dispositivo como a tus necesidades de carga o transferencia de datos.
- Necesidades de transferencia de datos: Para datos de alta velocidad, se recomienda USB-C o USB4. USB-A y Micro USB son opciones más lentas.
- Requisitos de carga: Los cables USB-C son ideales para la carga rápida, especialmente si tu dispositivo es compatible con USB Power Delivery (PD).
- A prueba de futuro: Si quieres preparar tus dispositivos para el futuro, optar por cables USB-C o USB4 garantizará la compatibilidad con nuevos dispositivos en los próximos años.
5. Conclusión
Los cables USB han evolucionado significativamente, ofreciendo velocidades más rápidas, mayor suministro de energía y mayor versatilidad. USB-A y Micro USB siguen utilizándose para los dispositivos heredados, pero USB-C se ha convertido en el estándar de la electrónica más moderna por su velocidad, potencia y compatibilidad. El nuevo USB4 está sentando las bases para la próxima generación de conectividad, ofreciendo una transferencia de datos ultrarrápida y un suministro de energía mejorado para dispositivos de alto rendimiento.
Comprender las diferencias entre estos cables le ayudará a elegir el adecuado para su dispositivo y requisitos de uso.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
P1: ¿Puedo utilizar un cable USB-A para cargar un dispositivo USB-C?
Sí, puedes usar un cable USB-A a USB-C, pero la carga será más lenta en comparación con el uso de un cargador USB-C.
P2: ¿Cuál es el cable USB más rápido?
USB4 proporciona las velocidades de transferencia de datos más rápidas, ofreciendo hasta 40 Gbps, lo que lo convierte en el estándar USB más avanzado.
P3: ¿Son todos los cables USB-C iguales?
No todos los cables USB-C son iguales. Algunos solo admiten la carga básica, mientras que otros admiten la transferencia de datos a alta velocidad y el suministro de energía. Comprueba siempre las especificaciones del cable que elijas.