Introduction
Universal Serial Bus (USB) technology has been a cornerstone in the realm of computer peripherals and data transfer for over two decades. With the advent of different versions and types, understanding the nuances between them becomes crucial for both consumers and professionals. This paper delves into the differences between USB 2.0 Type B and USB 3.0 Type B, exploring their technical specifications, compatibility, performance, and practical applications.
Technical Specifications
USB 2.0 Type B
Data Transfer Speed: USB 2.0, introduced in 2000, offers a maximum data transfer rate of 480 Mbps (Megabits per second). This speed is sufficient for many peripheral devices such as printers, scanners, and external hard drives that do not require high-speed data transfer.
Power Delivery: USB 2.0 can deliver up to 500 mA (milliamps) of current at 5V (volts). This power level is adequate for most peripheral devices but may fall short for more power-hungry devices.
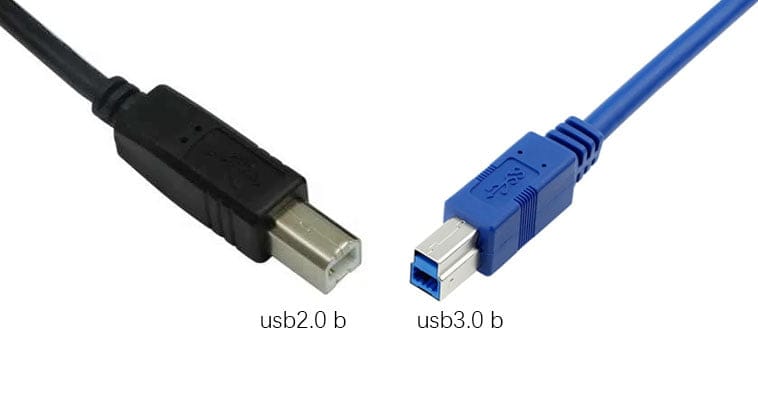
Physical Characteristics: The USB 2.0 Type B connector is characterized by its square shape with a slight bevel on the top corners. This design ensures a secure connection and prevents incorrect insertion.
USB 3.0 Type B
Data Transfer Speed: USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, was introduced in 2008 and offers a significant leap in data transfer speed, reaching up to 5 Gbps (Gigabits per second). This enhancement makes USB 3.0 suitable for high-speed data transfer applications, such as external SSDs (Solid State Drives) and high-resolution webcams.
Power Delivery: USB 3.0 can deliver up to 900 mA of current at 5V, providing more power to connected devices. This increased power delivery supports more demanding peripherals, such as larger external hard drives and devices with higher power consumption.
Physical Characteristics: The USB 3.0 Type B connector is larger than its USB 2.0 counterpart and includes an additional set of pins. This design allows for the higher data transfer rates and power delivery capabilities of USB 3.0. The connector is typically blue, distinguishing it from USB 2.0 connectors.
Compatibility and Interoperability
One of the significant advantages of USB technology is its backward compatibility. USB 3.0 Type B connectors are designed to be compatible with USB 2.0 ports, allowing users to connect USB 3.0 devices to older USB 2.0 ports. However, the data transfer speed and power delivery will be limited to USB 2.0 specifications when connected in this manner.
The physical differences between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 Type B connectors mean that a USB 2.0 Type B cable cannot be inserted into a USB 3.0 Type B port, but the reverse is possible. This design ensures that users do not accidentally connect devices in a manner that could lead to suboptimal performance or potential damage.
Performance Comparison
Data Transfer Rates
The most notable difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 Type B connectors is the data transfer rate. USB 3.0’s maximum speed of 5 Gbps is more than ten times faster than USB 2.0’s 480 Mbps. This higher speed is especially useful for large-data transfers, like computer backups, HD video file transfers, or external storage use.
Power Efficiency
USB 3.0’s ability to deliver up to 900 mA of current provides a significant advantage over USB 2.0’s 500 mA. This enhanced power delivery enables faster device charging and supports high-power peripherals without external power.
Practical Performance
In real-world applications, the performance benefits of USB 3.0 become evident when dealing with large files or data-intensive tasks. For example, transferring a 1GB file via USB 2.0 takes about 30 seconds, while the same transfer via USB 3.0 is completed in just a few seconds.This performance boost can significantly improve productivity and efficiency in environments where data transfer speed is critical.
Use Cases and Applications
Common Devices Using USB 2.0 Type B
USB 2.0 Type B connectors are commonly found on devices such as printers, scanners, and older external hard drives. These devices typically do not require the high data transfer rates or increased power delivery provided by USB 3.0.
Common Devices Using USB 3.0 Type B
Devices that benefit from higher data transfer speeds and greater power delivery use USB 3.0 Type B connectors. These include external SSDs, high-resolution webcams, and advanced docking stations. The increased capabilities of USB 3.0 make it the preferred choice for modern peripherals that demand higher performance.