High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) technology has become the standard for transmitting high-definition video and audio signals between devices. The type of HDMI cable used can significantly impact performance, especially in terms of bandwidth, signal integrity, and distance. This paper aims to compare HDMI fiber optic cables and regular HDMI cables (copper) by examining their technical specifications, performance, physical characteristics, and appropriate use cases.
Technical Specifications
HDMI Fiber Optic Cables
HDMI fiber optic cables use optical fibers to transmit data. These cables convert electrical signals into light signals, which are then transmitted through the optical fibers and converted back to electrical signals at the receiving end. Fiber optic HDMI cables can support higher bandwidths and longer transmission distances compared to regular HDMI cables.
Regular HDMI Cables (Copper)
Regular HDMI cables, also known as copper HDMI cables, use twisted pairs of copper wires to transmit data. These cables are designed to carry high-definition video and audio signals over short to medium distances. Copper HDMI cables are widely used due to their affordability and ease of installation.
Performance Comparison
Bandwidth and Data Transmission
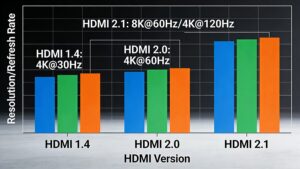
- HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: Fiber optic cables can support higher bandwidths, making them suitable for transmitting high-resolution video and audio signals, including 4K and 8K content. They can handle data rates up to 48 Gbps, which is required for HDMI 2.1 specifications.
- Regular HDMI Cables: Copper HDMI cables are generally limited to shorter distances and lower bandwidths. They can support data rates up to 18 Gbps, which is sufficient for HDMI 2.0 specifications, including 4K at 60Hz.
Signal Integrity and Distance
- HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: Fiber optic cables offer superior signal integrity over long distances. They are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), ensuring a stable and high-quality signal over distances up to 100 meters or more.
- Regular HDMI Cables: Copper HDMI cables are more susceptible to signal degradation over long distances. They are also prone to EMI and RFI, which can affect signal quality. The maximum effective distance for copper HDMI cables is typically around 15 meters.
Interference and Noise
- HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: Fiber optic cables are immune to electrical interference and noise, making them ideal for environments with high levels of EMI and RFI. This ensures a clean and reliable signal transmission.
- Regular HDMI Cables: Copper HDMI cables can pick up electrical interference and noise, which can degrade signal quality. Shielding and high-quality construction can mitigate some of these issues, but they are not as effective as fiber optic cables in noisy environments.
Physical Differences
Cable Construction
- HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: These cables are made of optical fibers, which are thin strands of glass or plastic that transmit light signals. They are typically more flexible and lighter than copper cables.
- Regular HDMI Cables: Copper HDMI cables consist of multiple twisted pairs of copper wires, which are thicker and heavier than optical fibers. They require more robust shielding to protect against interference.
Connectors
The connectors for both types of HDMI cables are the same, ensuring compatibility with HDMI ports on devices. However, the internal construction of the connectors may differ to accommodate the different transmission methods.
Use Cases and Applications
Home Entertainment Systems
- HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: Ideal for high-end home theater systems that require long cable runs and support for the latest video and audio formats.
- Regular HDMI Cables: Suitable for most home entertainment setups where cable runs are short and there is minimal interference.
Professional AV Installations
- HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: Preferred for professional AV installations, such as conference rooms, auditoriums, and digital signage, where long distances and high signal integrity are crucial.
- Regular HDMI Cables: Used in professional settings where shorter cable runs and lower resolutions are acceptable.
Industrial and Medical Applications
- HDMI Fiber Optic Cables: Used in industrial and medical environments where high levels of EMI and RFI are present, and where long-distance transmission is required.
- Regular HDMI Cables: Less commonly used in these environments due to their susceptibility to interference.
Future Trends and Compatibility
As display and audio technologies continue to advance, the demand for higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances will increase. HDMI fiber optic cables are well-positioned to meet these demands, providing a future-proof solution for high-definition signal transmission. Ensuring compatibility with existing devices and future standards will remain important considerations for both types of HDMI cables.
Conclusion
HDMI fiber optic cables and regular HDMI cables each have their advantages and limitations. Fiber optic cables offer superior performance in terms of bandwidth, signal integrity, and resistance to interference, making them ideal for long-distance and high-demand applications. Regular HDMI cables are more affordable and sufficient for most short-distance consumer applications. Understanding these differences allows consumers and professionals to choose the right cable type for their specific needs.