Introduction
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) technology has become the standard for transmitting high-definition audio and video between devices. With various versions and specifications available, choosing the right HDMI cable can significantly impact the quality of your multimedia experience. This paper aims to compare different HDMI versions by examining their specifications, performance, physical characteristics, and appropriate use cases.
Versions and Specifications
HDMI 1.0 to HDMI 1.4
- HDMI 1.0: Introduced in 2002, it supports a maximum data transfer rate of 4.95 Gbps and resolutions up to 1080p.
- HDMI 1.1: Added support for DVD-Audio.
- HDMI 1.2: Introduced support for One Bit Audio and improved compatibility with PC sources.
- HDMI 1.3: Increased the data transfer rate to 10.2 Gbps, supported higher resolutions, deep color, and new lossless audio formats.
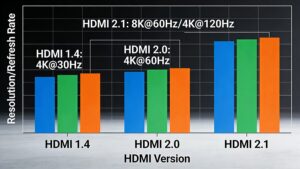
- HDMI 1.4: Introduced support for 4K resolutions at 30 Hz, an Audio Return Channel (ARC), and 3D video.
HDMI 2.0 and HDMI 2.1
- HDMI 2.0: Released in 2013, it supports 4K resolutions at 60 Hz, a data transfer rate of 18 Gbps, and enhanced audio and video capabilities.
- HDMI 2.1: Introduced in 2017, it supports 8K resolutions at 60 Hz, 4K at 120 Hz, a data transfer rate of 48 Gbps, Dynamic HDR, and enhanced eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel).
Performance Comparison
| Performance | HDMI 1.0 to 1.4 | HDMI 2.0 | HDMI 2.1 |
| Data Transfer Rates | Data transfer rates range from 4.95 Gbps to 10.2 Gbps | Supports a data transfer rate of 18 Gbps | Supports a data transfer rate of 48 Gbps |
| Resolution and Refresh Rates | Supports up to 1080p at 60 Hz and 4K at 30 Hz | Supports 4K at 60 Hz and 1080p at 240 Hz | Supports 8K at 60 Hz, 4K at 120 Hz, and 1080p at 240 Hz |
| Audio and Video Capabilities | Supports standard and high-definition audio formats, including Dolby Digital and DTS | Supports enhanced audio formats, including Dolby Atmos and DTS:X, and improved video capabilities | Supports Dynamic HDR, eARC, and enhanced audio and video synchronization |
Physical Differences
Cable Construction
- Standard HDMI Cables: Typically consist of four shielded twisted pairs of copper wires.
- High-Speed HDMI Cables: Use higher quality materials and better shielding to support higher data transfer rates and reduce signal degradation.
Connectors
- Type A: Standard HDMI connector used in most consumer electronics.
- Type C (Mini HDMI): Smaller connector used in portable devices.
- Type D (Micro HDMI): Even smaller connector used in compact devices.
- Type E: Automotive HDMI connector designed for in-vehicle use.
Use Cases and Applications
Home Entertainment Systems
- HDMI 1.0 to 1.4: Suitable for standard and high-definition TVs, Blu-ray players, and sound systems.
- HDMI 2.0: Ideal for 4K TVs, streaming devices, and advanced home theater systems.
- HDMI 2.1: Suitable for the latest 8K TVs and high-end home theater setups.
Professional and Commercial Applications
- HDMI 1.0 to 1.4: Used in conference rooms, classrooms, and digital signage.
- HDMI 2.0: Suitable for professional video production, broadcasting, and large-scale displays.
- HDMI 2.1: Ideal for cutting-edge commercial displays and installations requiring the highest resolution and performance.
Gaming and High-Performance Applications
- HDMI 1.0 to 1.4: Sufficient for older gaming consoles and PCs.
- HDMI 2.0: Suitable for modern gaming consoles and high-performance PCs.
- HDMI 2.1: Ideal for the latest gaming consoles, high-end gaming PCs, and virtual reality setups.
Future Trends and Compatibility
As HDMI technology continues to evolve, newer versions like HDMI 2.1 offer significant improvements in data transfer rates, resolution, and audio-visual capabilities. Ensuring compatibility with existing devices and future standards will remain important considerations for consumers and professionals alike.
Conclusion
HDMI cables come in various versions, each offering distinct advantages and limitations. HDMI 1.0 to 1.4 provide sufficient performance for standard and high-definition applications, while HDMI 2.0 and 2.1 offer enhanced capabilities for 4K and 8K resolutions, respectively. Understanding these differences allows consumers and professionals to choose the right HDMI cable for their specific needs.