In the ever – evolving landscape of network connectivity, the choice between Cat 7 and Cat 8 Ethernet cables can be a perplexing one. Both cables represent significant advancements in Ethernet technology, but they are tailored to different needs. Let’s first start with a side – by – side comparison table to grasp their core differences at a glance, then delve into detailed analyses to help you make an informed decision for your network setup.
Cat 7 vs. Cat 8: Core Specs Comparison Table
|
Key Feature
|
Cat 7 Ethernet Cable
|
Cat 8 Ethernet Cable
|
|
Maximum Speed
|
10 Gbps (10,000 Mbps)
|
Up to 40 Gbps (25 Gbps common for shorter runs)
|
|
Bandwidth
|
600 MHz
|
2000 MHz
|
|
Shielding
|
Individual pair shielding + overall shielding
|
Individual pair shielding + overall shielding + plug shielding
|
|
Max Length (at full speed)
|
100 meters (for 10 Gbps)
|
30 meters (for 25/40 Gbps)
|
|
Common Connectors
|
RJ – 45 (GigaGate45 for full performance)
|
TERA, GG45 (optimized for high – speed)
|
|
Cost (Per Meter, Approx.)
|
2 – 5
|
8 – 15
|
|
Ideal Use Cases
|
Home labs, small offices, 4K streaming, gaming
|
Data centers, 8K editing, high – performance computing
|
|
Future Compatibility
|
Backward – compatible (Cat 6a/Cat 6), limited for ultra – high – speed future needs
|
Backward – compatible, designed for 5G/cloud/8K future demands
|
Speed and Bandwidth
Cat 7:
- Offers a maximum speed of 10 Gbps (10,000 Mbps). This speed is more than sufficient for most high – end home applications, such as 4K video streaming, online gaming, and large – file transfers within a local network.
- Has a bandwidth of 600 MHz. This frequency range allows for efficient data transmission at high speeds over the cable.
Cat 8:
- Takes speed to the next level with a maximum speed of up to 40 Gbps (in some cases, 25 Gbps is also common). This makes it ideal for data – intensive applications like data center operations, high – performance computing clusters, and real – time 8K video editing.
- Boasts a much wider bandwidth of 2000 MHz. The broader frequency range enables the cable to handle the massive amounts of data associated with its high – speed capabilities.

Shielding
Cat 7:
- Features a high – level of shielding. It typically has individual shielding for each twisted pair of wires within the cable, along with an overall shielding layer. This design helps to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, ensuring a stable and reliable data connection. The shielding is crucial in environments with a lot of electronic devices, such as industrial settings or data centers.
- The shielding in Cat 7 cables helps to reduce signal degradation, allowing for consistent performance even in challenging electromagnetic environments.
Cat 8:
- Builds on Cat 7’s shielding and offers even better protection. In addition to individual pair shielding and an overall shielding layer, Cat 8 cables often have additional shielding at each plug. This extra shielding further reduces signal degradation and improves the cable’s performance in high – interference environments.
- The enhanced shielding in Cat 8 makes it the go – to choice for applications where maintaining a pristine, high – speed data connection is critical, like in financial trading floors or research institutions conducting data – intensive experiments.
Cable Length
Cat 7:
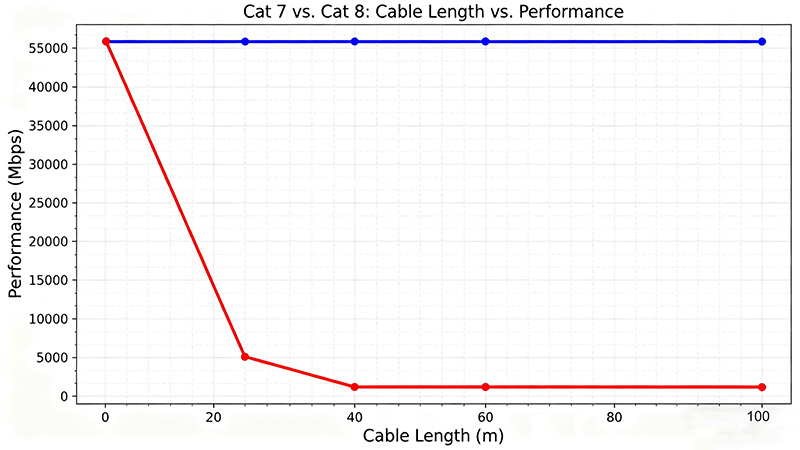
- Supports a maximum cable length of 100 meters for 10 Gbps Ethernet connections. This length is suitable for most home and office network setups, where devices are typically within a reasonable distance of each other. For example, in a standard – sized office building, Cat 7 cables can be used to connect workstations, servers, and network switches across multiple rooms on the same floor.
- The 100 – meter limit ensures that the cable can maintain its high – speed performance without significant signal loss over the distance.
Cat 8:
- Has a reduced maximum cabling length of 30 meters for 25 Gbps and 40 Gbps Ethernet connections. Beyond this distance, the cable’s performance may start to decline due to signal attenuation. However, within this 30 – meter range, Cat 8 can deliver its lightning – fast speeds.
- This shorter length makes Cat 8 more suitable for use within data centers, where devices are often located in close proximity to each other. For instance, it can be used to connect servers to top – of – rack switches in a data center rack.
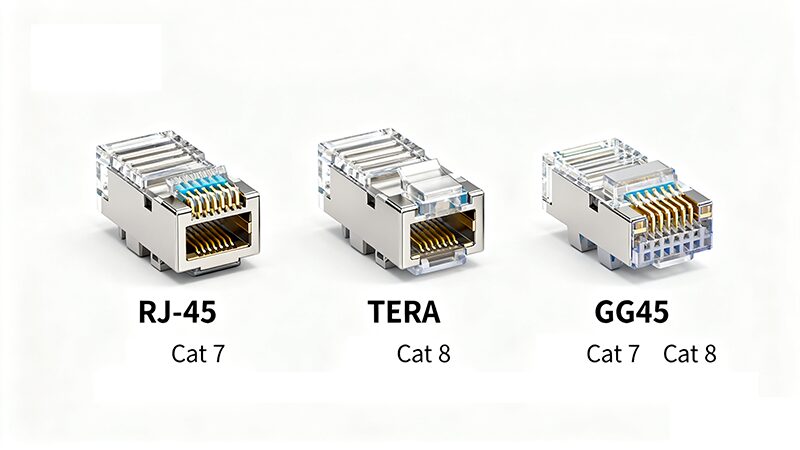
Connector Type
Cat 7:
- Usually uses the familiar RJ – 45 connectors, which are widely used in networking. The advantage of this is that it is compatible with a large number of existing network devices, making it easier to integrate into existing network setups. For example, if you are upgrading your home network from a lower – category cable to Cat 7, you may not need to replace all of your network device connectors.
- However, to fully utilize Cat 7’s higher performance capabilities, some specialized connectors like GigaGate45 may be required in certain applications.
Cat 8:
- Often employs newer connector types such as TERA or GG45. These connectors are designed to offer improved performance and durability compared to traditional RJ – 45 connectors. They are optimized to handle the high – speed data transmission and enhanced shielding features of Cat 8 cables.
- While these connectors may require some additional investment when setting up a new network, they are essential for ensuring that Cat 8 cables can deliver their maximum performance.

Cost
Cat 7:
- Generally, Cat 7 cables are more affordable compared to Cat 8. This makes them a popular choice for those who want to upgrade their network to a high – speed, reliable connection without breaking the bank. For example, in a small – to – medium – sized business looking to upgrade its network infrastructure, Cat 7 can provide a cost – effective solution for achieving 10 Gbps speeds.
- The cost – effectiveness of Cat 7 also extends to installation, as the use of common RJ – 45 connectors may reduce the need for specialized tools and labor.
Cat 8:
- Due to its advanced technology, higher performance capabilities, and specialized connectors, Cat 8 cables are typically more expensive. The cost of Cat 8 cables can be a significant factor, especially for large – scale installations. However, for applications where the highest speed and performance are non – negotiable, such as in large data centers or high – end enterprise networks, the cost may be justifiable.
- The cost of Cat 8 also includes the potential need to upgrade network devices to support the higher – speed capabilities and specialized connectors.
Future Compatibility
Cat 7:
- Is backward compatible with previous Ethernet standards, such as Cat 6a and Cat 6. This means that you can use Cat 7 cables in existing home or office networks with older devices, and still enjoy the benefits of its higher speed and better shielding. For example, if you have a mix of newer and older computers in your office, Cat 7 can be used to connect all of them, providing a seamless upgrade path.
- However, as technology continues to advance, Cat 7 may not be able to keep up with the very highest – speed requirements of future – proofed networks.
- Is also backward compatible with older Ethernet category standards. But it is specifically designed for high – speed, high – bandwidth applications of the future. If you are planning a new network installation or a major upgrade and want to future – proof your network for the next few years, Cat 8 is a great option. For example, with the increasing adoption of technologies like 5G backhaul, cloud computing, and high – definition virtual reality, Cat 8 can provide the necessary speed and performance.
- The use of Cat 8 in new installations can ensure that your network is well – equipped to handle emerging applications and technologies that demand extremely high data transfer rates.