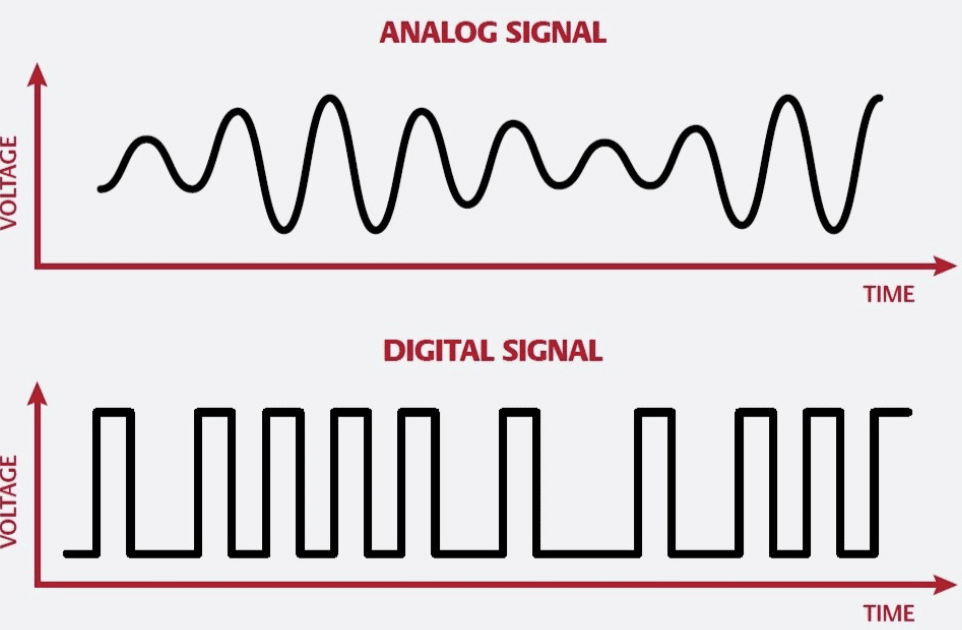
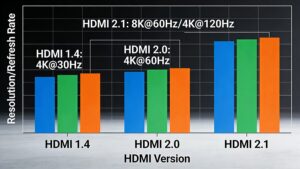
Analog vs. Digital Cables: Core Differences Explained
In today’s tech-driven world, understanding the distinction between analog and digital cables is critical for optimizing device performance. This guide breaks down their differences, applications, and SEO-optimized insights to help users make informed decisions.
Fundamental Concepts: How Analog and Digital Cables Work
Core Differences: Performance and Applications
User-Centric Insights: Choosing the Right Cable